10 important considerations for NLP labeling
When you perform natural language processing (NLP) labeling to create machine learning models, you want the data labeling tool you choose to have specific functionality so that you can create a high-quality dataset to train or fine-tune your model.
We’ve identified the ten most important features that you need to consider when starting with an NLP labeling tool.
1. Label text spans
You must be able to label text spans with the tool that you choose for NLP labeling. Whether you’re trying to label entire words, sentences, or some other span of text, this is the most basic feature you need.

2. Label intersecting and overlapping text
Depending on the type of NLP labeling that you’re performing, you likely need to be able to label intersecting and overlapping text, for example, to label both full words and morphemes.

3. Label partial words
For some NLP labeling use cases, you might need to label partial words. For example, training a model to recognize prefixes, suffixes, or compound words. If you’re limited to text spans that are at least a full word, you won’t be able to perform your labeling tasks.
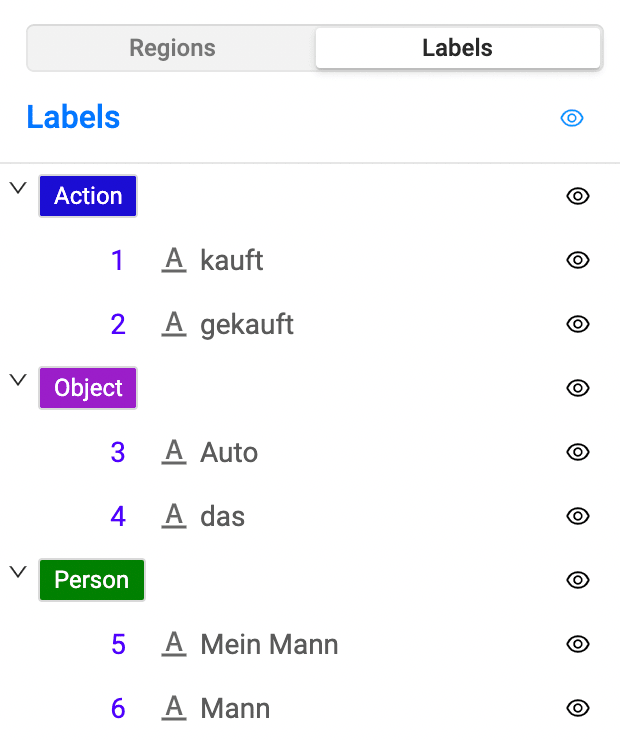
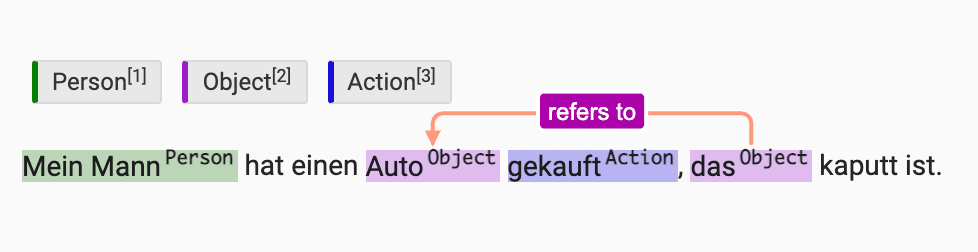
4. Identify and label relations between text spans
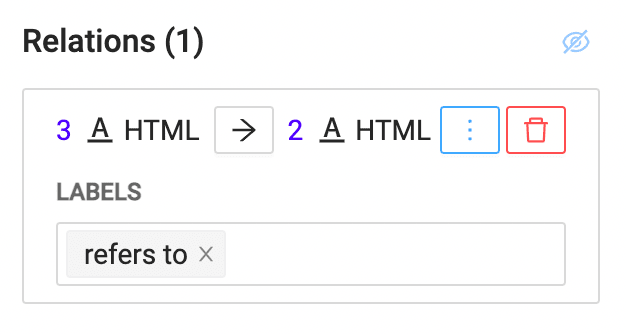
For most NLP labeling tasks, you need to be able to identify relations between text spans so that you can train your natural language understanding (NLU) model on those relations.
More importantly, after you identify those relations as part of your NLP labeling, you need to be able to label those relations. Define what makes those relations relevant to your NLU model by labeling subject-verb agreement interactions, or labeling which noun a relative pronoun refers to.
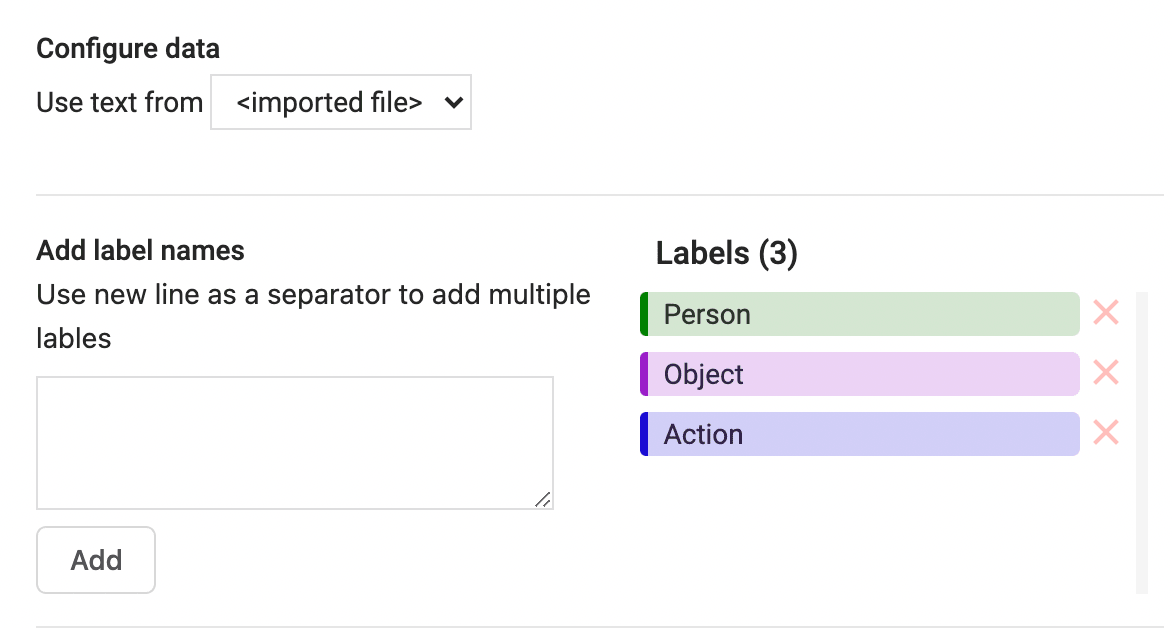
5. Define consistent labels
Whether you’re defining an ontology or terminology, you want the labels that annotators apply to the text to be consistent across all NLP labeling activities. Make sure that the schema that you define for labeling requires a consistent list of labels to use across all labeling tasks.
6. Support for many classes
You want your labels to be consistent, but you also want the flexibility to choose from a wide array of classification options. If you can add dozens or even hundreds of labels for annotators to choose from, and if those annotators can filter and search for the correct labels when annotating the data, you can complete your large scale NLP labeling project faster.
7. Semantic classification
Beyond labeling portions of the text as a specific part of speech or morpheme, you might also want to classify the semantic meaning of the text. A tool that allows you to classify meaning, as well as highlight and label text spans, is a flexible tool that can support a number of NLP labeling tasks.
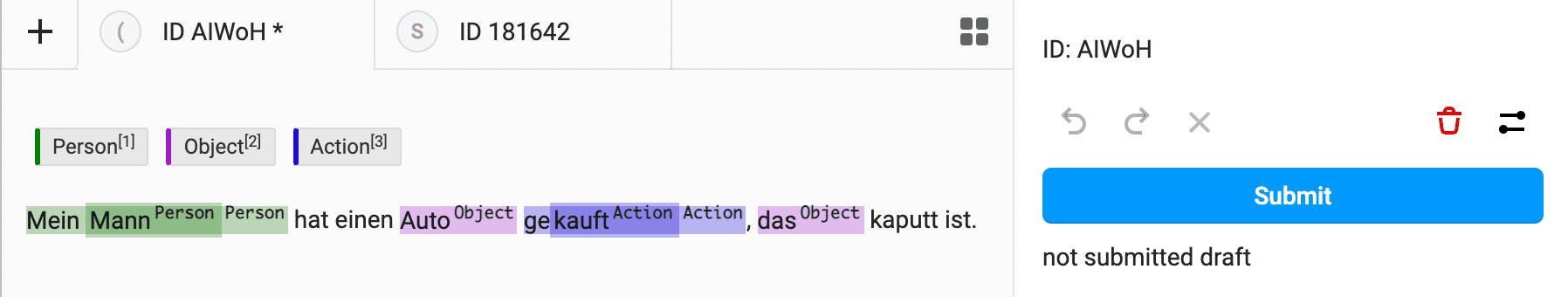
8. Save draft annotations
When labeling long text samples, you want the ability to take a break from labeling and return where you left off. If you can save draft annotations, it is easier to complete more time-consuming NLP labeling tasks.
9. Support multiple annotators
In order to ensure high-quality annotations, you want to make sure that whichever tool you choose for your NLP labeling, it supports multiple annotators. Often, the more people that label a task, the higher quality the annotations are likely to be.
10. Non-English labeling capabilities
Not all natural language processing happens in English. A tool that can support non-English languages and special characters is important to capture the global and expressive nature of text-based communication in the modern world.
Conclusion
There are a lot of data labeling tools available. It’s important to carefully assess the best one to help you perform NLP labeling. We hope that this list of important functionality can help you define the requirements for your next NLP labeling tool!
